
What is the purpose of an organisation?
Professor Nick Barter explores the evolution of corporate purpose, from shareholder focus to stakeholder inclusion, emphasising its strategic importance and providing guidance for modern organisations.
The bushfires of the summer of 2019-2020 which covered more than 10 million hectares, were exacerbated by human intervention. In this climate emergency, business as usual is not an option, and hazard reduction burning and backburning must be re-evaluated.
Once many of these fires got out of control, the agencies switched to ‘back’ burning ahead of the fire front, exacerbating the problem. This in turn emboldened local landowners to burn their properties (as was the case with the 30,000 hectares burnt at Ebor, NSW).
In NSW, since the fires, the Kalang River catchment in the shire of Bellingen has become one of the last strongholds for koala and other endangered ‘apex’ species (species which help maintain ecological integrity). There were plans to log the catchment, which were resisted by local residents. Despite this, there is always pressure to burn the catchment to protect the town.
But if we kill apex species, we convert ecosystems (not to mention undermine the quality of the municipal water supply). A good example is the destruction of bison in North America.
The tallgrass prairie, its primary habitat—which once covered millions of acres—is now reduced to a few fragments. Returning the bison, it has been shown, significantly aids regeneration.
In the case of the Kalang, we need to protect these forests from fire, not burn them, and we should do that by:
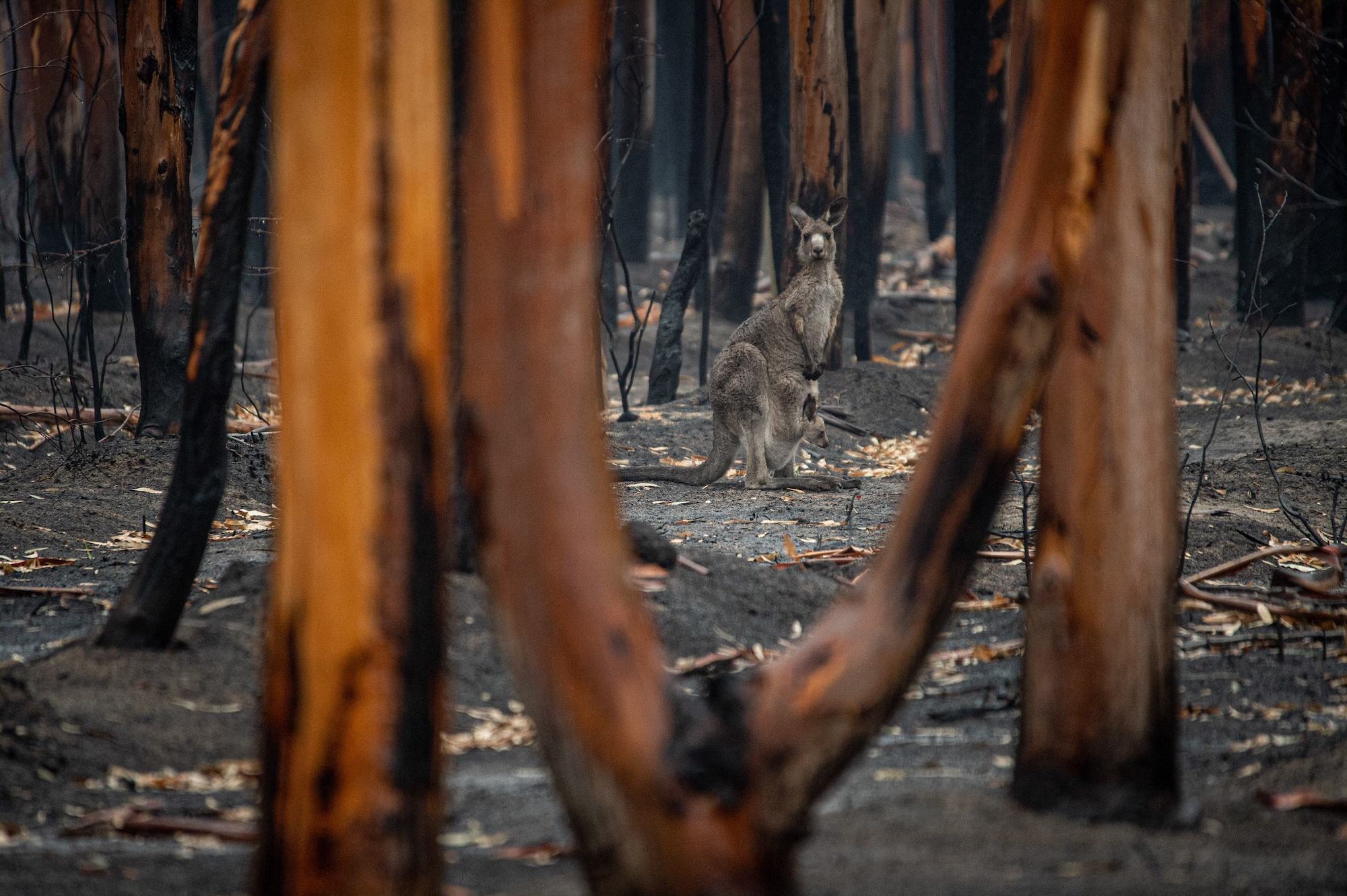

Supporters of burning claim it’s better to stop a hot burning fire consuming everything in front of it, even if that means creating a narrow corridor of low–level burnt material, as this means the fire runs out of fuel.
We cannot stop these fires. They are a consequence of climate change. Therefore, the best response is to change our behaviour in the face of the inevitable, and not deny its reality.
We need to learn how to cope with changed conditions (in climate change policy, this is referred to as adaptation). We also need to give the planet a break from extractive and destructive human activities, particularly the combustion of fossil fuels and the degradation of the natural environment, and prevent further exacerbation of the problem (also known as mitigation).
This is the context I believe this debate is missing. I admire and respect all our firefighters, and I hope they get the resources they need to extinguish the fires, not make more. Those of us living within semi-natural environments have to take responsibility for our own properties. Town residents need to have secure municipal perimeters—and we all need to implement other measures, such as sprinkler systems. We can no longer afford to lay waste to everything around us in the vain hope things will get better.
 Dr Timothy Cadman specialises in the governance of sustainable development, environmental politics and policy, climate change, natural resource management including forestry, responsible investment and institutional performance.
Dr Timothy Cadman specialises in the governance of sustainable development, environmental politics and policy, climate change, natural resource management including forestry, responsible investment and institutional performance.
Follow Tim on Twitter

Professor Nick Barter explores the evolution of corporate purpose, from shareholder focus to stakeholder inclusion, emphasising its strategic importance and providing guidance for modern organisations.
Celebrated author Benjamin Law has worked in the media industry for over a decade. He hates thinking of himself as a ‘diversity hire’. ‘I belong in this room,’ I told myself. I’m not a token – despite being called that so many times in my career that I’ve lost count. I’ve earned my place.

The National Rugby League’s inaugural Las Vegas Round attracted over 40,000 fans and showcased rugby league to Americans. To capitalise, the NRL should focus on awareness, celebrity involvement, American ownership, and expanding the women’s game says Griffith University’s Dr Jason Doyle.